The Taxpayer First Act of 2019 is redesigning how the IRS works with taxpayers, even though it may take a while for many of the provisions to take effect.
Some experts have highlighted the following aspects of the bill as especially important:
An independent appeals process. Taxpayers and small businesses will be able to challenge the IRS’ position without undertaking the cost and expenses of court. IRS Appeals will be an independent unit that grants taxpayers access to case files. Taxpayers will be able to protest if denied an appeal.
Innocent spouse treatment. The new law requires the U.S. Tax Court to take a fresh look at innocent spouse cases without taking previous decisions into account.
Modification of procedures for issuance of third-party summons. This is an important protection for taxpayers, especially small-business owners. It discourages the IRS from bypassing the taxpayer and contacting third parties — such as financial institutions — instead for information. The IRS should give taxpayers a meaningful opportunity to provide the information it is seeking prior to its contacting third parties. In practice, the IRS should provide the taxpayer with an understanding of what the issue is, what information is being requested and how the requested information relates to the issue.
Office of the National Taxpayer Advocate. The Taxpayer First Act has taken a strong approach with the Advocate’s issuance of Taxpayer Advocate Directives, which focus on systemic problems taxpayers deal with. Once they are issued by the Advocate, the IRS should comply within 90 days. The Advocate Annual Report will identify any TAD that is not honored by the IRS.
Credit card payments. The IRS is now allowed to directly accept credit and debit card payments for taxes; the taxpayer must pay any processing fees. The Act also requires the IRS to try to minimize processing fees when entering into contracts with the credit card companies.
Whistle blower reforms. The Act provides protections from retaliation and allows for better communication with whistle blowers about the status of their claims.
Cyber-security and identity protection. The IRS will now have to let taxpayers know whether it suspects there is evidence of identity theft. The Agency will explain to taxpayers how to file a report with police and how to protect themselves against additional harm resulting from the identity theft.
Taxpayer Act levels the playing field
Rep. Kevin Brady, R-Texas, ranking member of the Ways and Means Committee, was quoted as saying the Act “levels the playing field to ensure taxpayers have the same information as the agency, better protects our taxpayers’ information, and reins in past IRS abuses to guarantee families and local businesses never have to fear having their accounts and property seized without fair and due process.”
As with many new laws, it will take some time to see what specifically the effects are. The legal provisions are complex and will require interpretation over time. We’ll be keeping an eye on the developments.
We’ve got your back
The new tax code is complex and every taxpayer’s situation is different – so don’t go it alone! Contact KRS managing partner Maria Rollins at mrollins@krscpas.com or 201.655.7411 to discuss your situation.


 Get the most from your vacation home rental property by knowing the tax rules
Get the most from your vacation home rental property by knowing the tax rules Does your home office qualify for a tax deduction?
Does your home office qualify for a tax deduction? Deducting expenses for medical and dental care is easier when you know the rules
Deducting expenses for medical and dental care is easier when you know the rules New Jersey, New York, and Connecticut from utilizing workarounds to evade the new $10,000 limit on state and local tax (“SALT”) deductions.
New Jersey, New York, and Connecticut from utilizing workarounds to evade the new $10,000 limit on state and local tax (“SALT”) deductions. However, they have to be careful: one small mistake and an IRA’s tax advantages disappear.
However, they have to be careful: one small mistake and an IRA’s tax advantages disappear. on payroll.
on payroll.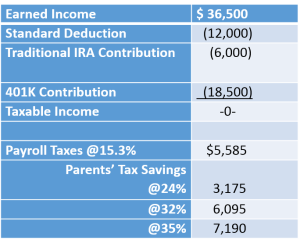 If the entity is an LLC instead of an S-Corp, and your child is under 18, add back the payroll taxes of $5,585 to get your tax saving potential.
If the entity is an LLC instead of an S-Corp, and your child is under 18, add back the payroll taxes of $5,585 to get your tax saving potential. If you were married this past year, congratulations!
If you were married this past year, congratulations! Even when you take the customer to court and you still don’t get your money, there’s a way to make lemonade from this lemon of a customer.
Even when you take the customer to court and you still don’t get your money, there’s a way to make lemonade from this lemon of a customer. Unfortunately, 2018 has been another year of major disasters due to hurricanes, fires, and floods. As taxpayers turn to the process of restoring property, some may be considering whether a 1033 exchange is more relevant than a 1031 exchange.
Unfortunately, 2018 has been another year of major disasters due to hurricanes, fires, and floods. As taxpayers turn to the process of restoring property, some may be considering whether a 1033 exchange is more relevant than a 1031 exchange.