 Accounting for the growing cannabis industry is unique. Here’s why.
Accounting for the growing cannabis industry is unique. Here’s why.
The goal of any accounting system is to ensure that accurate financial information is available timely to users. An appropriate system will include processes and procedures for collecting, recording and classifying data and will assist in preventing and detecting waste or, even worse, fraud.
So why is accounting for the growing cannabis industry so unique?
Management, investors and other financial statement users require the same accurate financial information as any other industry. However, in this growing industry, businesses must comply with strict state and federal regulations to avoid substantial penalties or even the risk of losing their business.
Cannabusiness accounting and compliance
Proper and adequate accounting systems and controls are even more critical in a cannabis business where the business “touches the plant.” Growers, processors and distributors have unique accounting and compliance needs unlike any other industry. The potential for large cash transactions and banking restrictions common in the industry further emphasize the need for proper accounting controls and procedures.
As states begin to legalize marijuana for medical and recreational use, businesses will need to consider the unique challenges the industry faces at the onset. The federal government considers business operations in this space to be “trafficking in controlled substances.” As such, proper accounting and reporting should incorporate the nuances of Internal Revenue Code Sec. 280E and 471 relating to cost accounting and inventory. In addition, state regulations require industry tracking and reporting of “seed to sale.” Most states with legalized marijuana industry require businesses to have inventory control and reporting systems in place as well as an interface with state mandated tracking systems. Therefore, the accounting system must provide reports and analysis to support compliance with federal and local regulations.
In this highly regulated environment, the business can be audited at any moment. All records must be available and in order to prove compliance with state and federal regulations. Furthermore, the accounting for businesses in this industry will need to provide for transactions to and from related entities, segment or separate “lines of business” reporting and consolidation. Business structures often include related entity relationships and investments. These advanced accounting issues are uncommon for most young or start-up businesses in other industries.
While many businesses entering the Cannabusiness space are new businesses, they cannot approach their accounting and bookkeeping in a manner often seen with new business start-ups. It’s common for a start-up to lack a proper accounting system and accounting controls before the business is up and running. A Cannabusiness business must have their system and controls in place well before they start operations.
We’ve got your back
Cannabusiness is a developing industry with many complicated factors. If you’re starting a business in this space, don’t go it alone! Contact Managing Partner Maria Rollins at mrollins@krscpas.com or 201.655.7411 to discuss your situation.

 Accounting for the growing cannabis industry is unique. Here’s why.
Accounting for the growing cannabis industry is unique. Here’s why.

 A passive loss from a real estate activity occurs when your rental property’s expenses exceeds its income. The undesirable consequence of passive losses is that a taxpayer is only allowed to claim a certain amount of losses on their tax return each year.
A passive loss from a real estate activity occurs when your rental property’s expenses exceeds its income. The undesirable consequence of passive losses is that a taxpayer is only allowed to claim a certain amount of losses on their tax return each year. The new Tax Cuts and Jobs Act amends the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) to reduce tax rates and modify policies, credits, and deductions for individuals and businesses. It is the most sweeping update to the U.S. tax code in more than 30 years, and from what we’re seeing, it impacts everyone’s tax situation a bit differently.
The new Tax Cuts and Jobs Act amends the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) to reduce tax rates and modify policies, credits, and deductions for individuals and businesses. It is the most sweeping update to the U.S. tax code in more than 30 years, and from what we’re seeing, it impacts everyone’s tax situation a bit differently.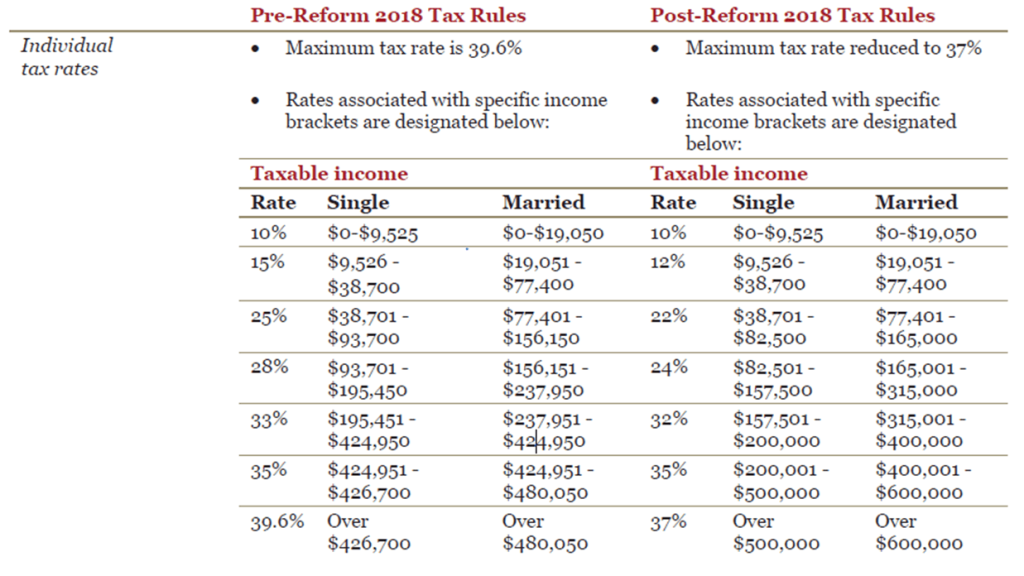




 Selling a vehicle outright or trading it in towards a new vehicle usually involves analyzing the economics of the transaction. However, tax factors can start to complicate things if that vehicle was used in your business.
Selling a vehicle outright or trading it in towards a new vehicle usually involves analyzing the economics of the transaction. However, tax factors can start to complicate things if that vehicle was used in your business.
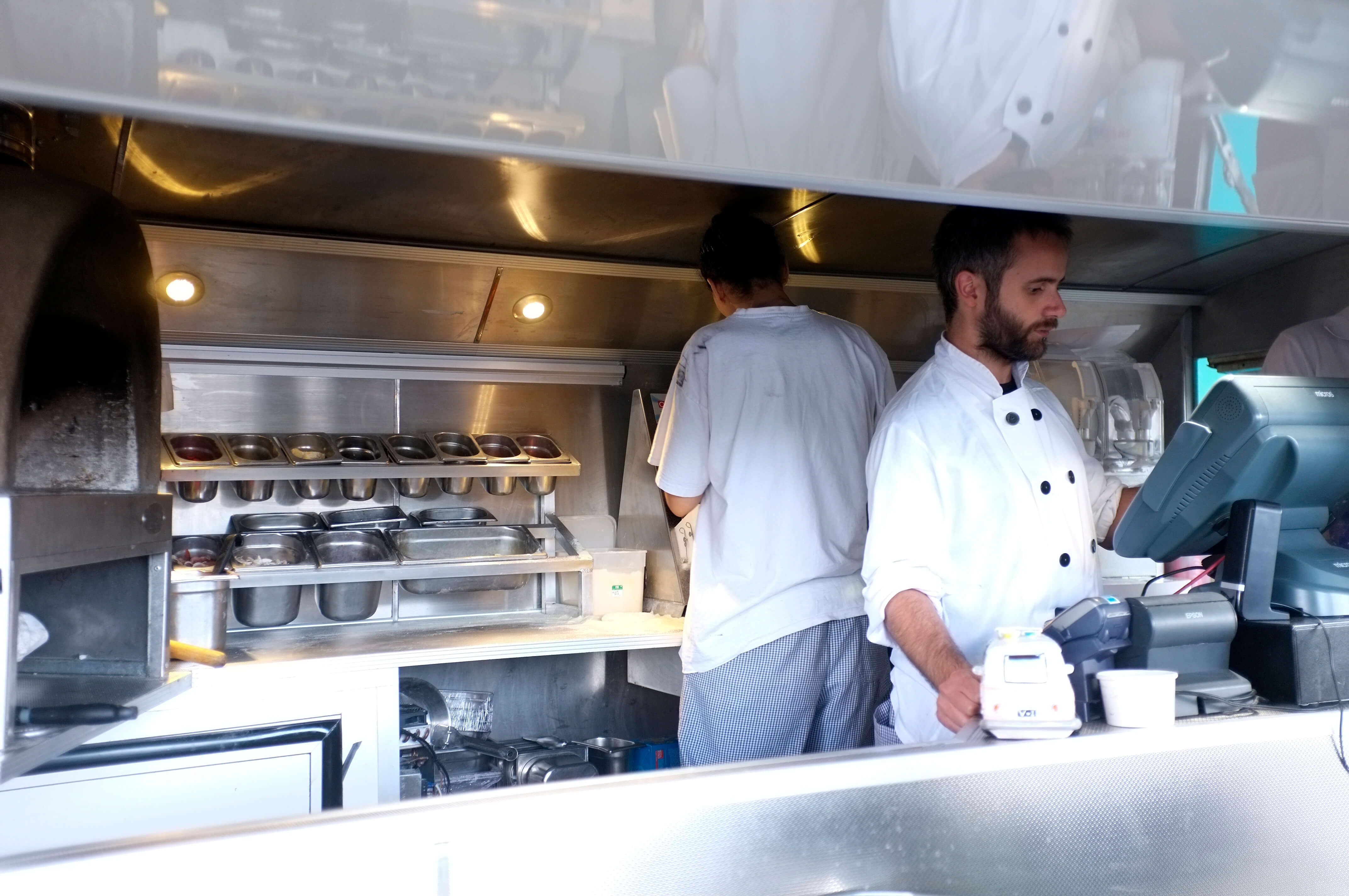 Congratulations! You started a food service business in a food truck or completed a proof of concept on wheels or in temporary space. Now you have made a business decision to expand and operate a brick-and-mortar location.
Congratulations! You started a food service business in a food truck or completed a proof of concept on wheels or in temporary space. Now you have made a business decision to expand and operate a brick-and-mortar location.
 Making charitable contributions is a great way to reduce your taxable income. The most common type of donation is a monetary contribution. Taxpayers are allowed to make tax deductible monetary contributions to qualified organizations in amounts up to 50% of adjusted gross income.
Making charitable contributions is a great way to reduce your taxable income. The most common type of donation is a monetary contribution. Taxpayers are allowed to make tax deductible monetary contributions to qualified organizations in amounts up to 50% of adjusted gross income.